Quiz_Offshoring
国际贸易测试代写 1. The provision of a service or input component part that is assembled into a final good at another location is known as: a. barter.
1.
The provision of a service or input component part that is assembled into a final good at another location is known as:
a. barter.
b. component trade.
c. intermediate trade.
d. offshoring.
2.
An example of offshoring is when:
a. Boeing contracts with companies across the world to manufacture components for its 787 Dreamliner aircraft.
b. Boeing assembles its 787 Dreamliner in Everett, Washington.
c. Boeing contracts with another American company to construct sections of the 787 Dreamliner’s fuselage in Charleston, South Carolina.
d. Boeing sends workers to Japan to learn the technology to assemble its 787 Dreamliner.
3. 国际贸易测试代写
Firms consider offshoring mainly to decrease their:
a. labor costs.
b. transportation costs.
c. construction costs.
d. “trade costs.”
4.
Which of the following is an example of offshoring?
a. Intel undertakes direct foreign investment in China to produce computer chips for the Chinese market.
b. Ford establishes a factory in Germany to produce automobiles for the European market.
c. General Motors moves assembly operations for Chevrolets from Detroit to its plant in Mexico.
d. Nike closes its Indonesian factory and moves production to the United States to produce tennis shoes for the U.S. market.
5. 国际贸易测试代写
What is the difference between final goods and intermediate goods?
a. Final goods require further processing before consumption.
b. Intermediate goods are sold directly to the consumer.
c. Intermediate goods are inputs for other goods.
d. Final goods require further processing before consumption, while intermediate goods are inputs for other goods.
6.
Which of the following is the correct ranking (first to last) of the value chain by order of production?
a. component production, assembly, marketing and sales, R&D
b. component production, marketing and sales, assembly, R&D
c. R&D, component production, assembly, marketing and sales
d. R&D, marketing and sales, component production, assembly
7. 国际贸易测试代写
Which of the following is NOT a consideration that firms should include in deciding whether to offshore part of its value chain of activities?
a. higher foreign costs of construction, electricity, and fuel
b. higher foreign taxes
c. higher transportation costs to ship the offshored product to the home country
d. relatively higher costs of foreign skilled labor
8.
Which of the following is a “trade cost” that firms need to consider when making offshoring decisions?
a. higher prices of utilities (electricity, fuel) in other countries
b. higher costs of construction of a plant in other countries
c. higher costs associated with poor communication and transportation
d. lower wages paid to low-skilled workers
9. 国际贸易测试代写
The offshoring decision revolves around:
a. the level of domestic opposition to the idea of offshoring.
b. the level of technology at home and abroad.
c. a comparison of the value-added, the marginal costs, and the trade costs of a firm’s activities at home versus abroad.
d. labor costs abroad versus in the home market.
10.
Reduction in trade costs will tend to:
a. discourage offshoring.
b. discourage foreign production.
c. encourage offshoring.
d. have no immediate effect on offshoring decisions.
11. 国际贸易测试代写
Which of the following groups of Ford Motor Company employees will be most adversely affected by Ford’s offshoring of part of its operations to Mexico?
a. Ford engineers and scientists
b. Ford accountants
c. Ford managers
d. Ford assembly-line workers
12.
Figure: A Firm’s Production with and Without Offshoring 1

In the graph, which line shows the initial level of production for this firm?
a. Y1
b. Y0
c. the bowed-out curved line
d. the vertical axis
13. 国际贸易测试代写
Figure: A Firm’s Production with and Without Offshoring 1
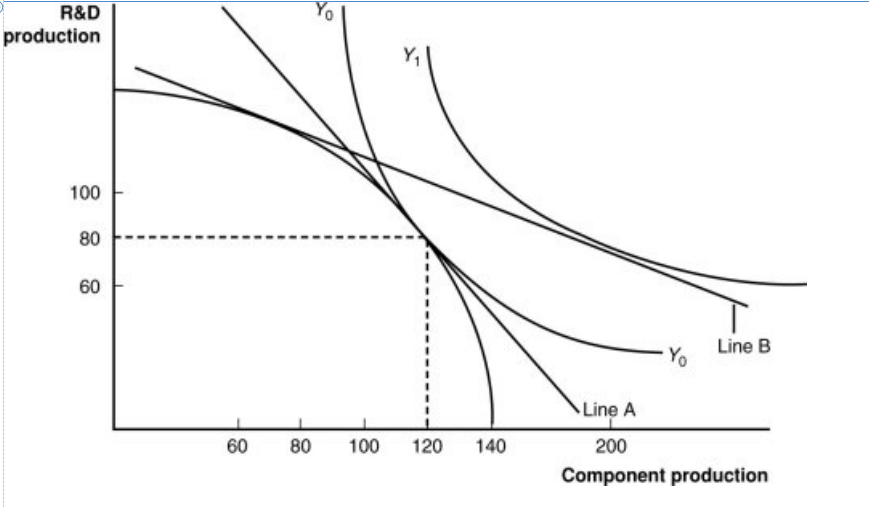
In “no-offshoring” equilibrium, how many units of component production will there be?
a. 60
b. 80
c. 100
d. 120
14.
Figure: A Firm’s Production with and Without Offshoring 1
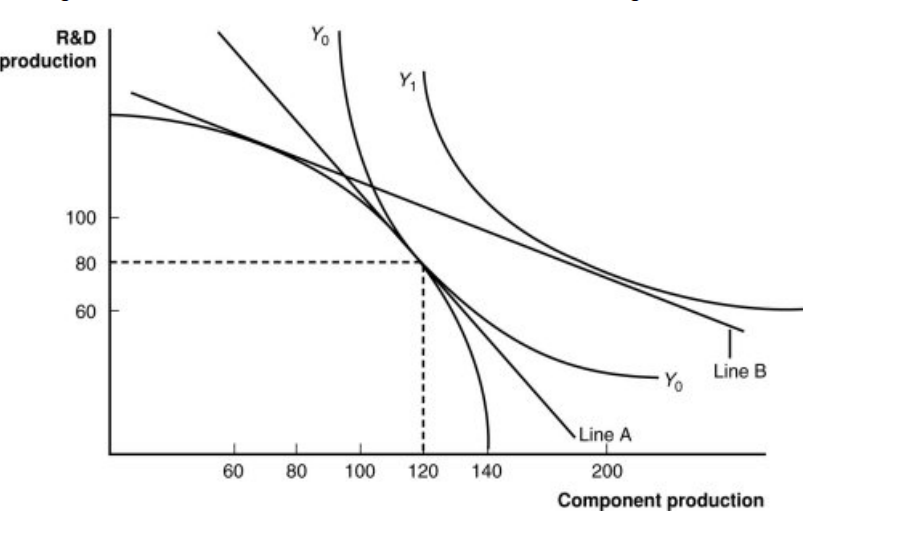
In a “no-offshoring” equilibrium, how many units of R&D production will there be?
a. 60
b. 80
c. 100
d. 120
15. 国际贸易测试代写
Figure: A Firm’s Production with and Without Offshoring 1
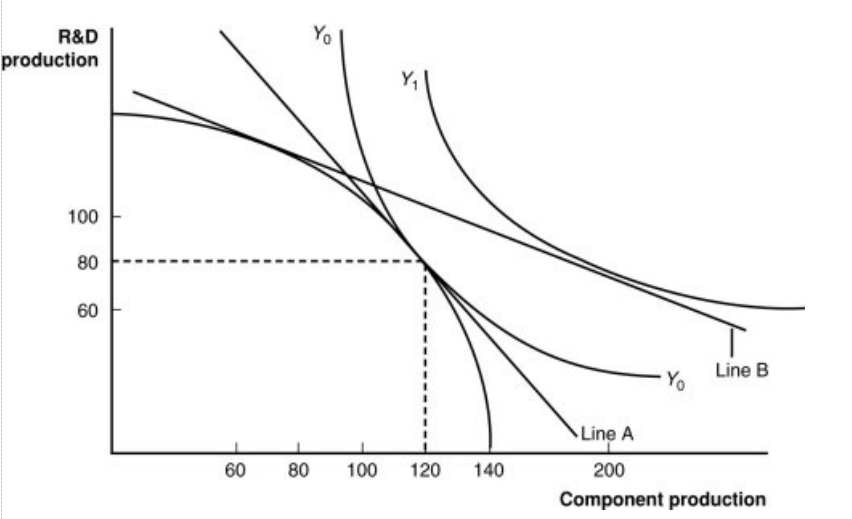
Assuming that skilled workers are needed for R&D and unskilled workers are needed for components, if there is an increase in the price for research and development products, this firm will _____ those products, the demand for _____ will increase, the wages of these workers will rise, and the price line in the graph will _____.
a. import; unskilled workers; become steeper
b. export; skilled workers; become flatter
c. neither import nor export; both workers in the same proportion; not change
d. import; unskilled workers; become flatter
16.
Figure: A Firm’s Production with and Without Offshoring 1
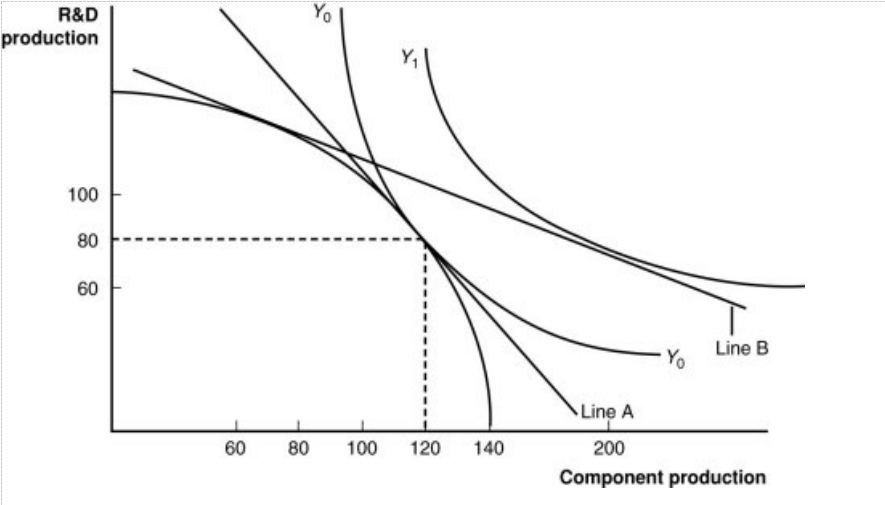
If component parts become relatively cheaper abroad, this firm will have an incentive:
a. to offshore (import) components and export R&D.
b. to import R&D products along with skilled workers.
c. to export both R&D and component parts.
d. to make few changes in the trading regime because of the delicate international balance.
17. 国际贸易测试代写
Figure: A Firm’s Production with and Without Offshoring 1
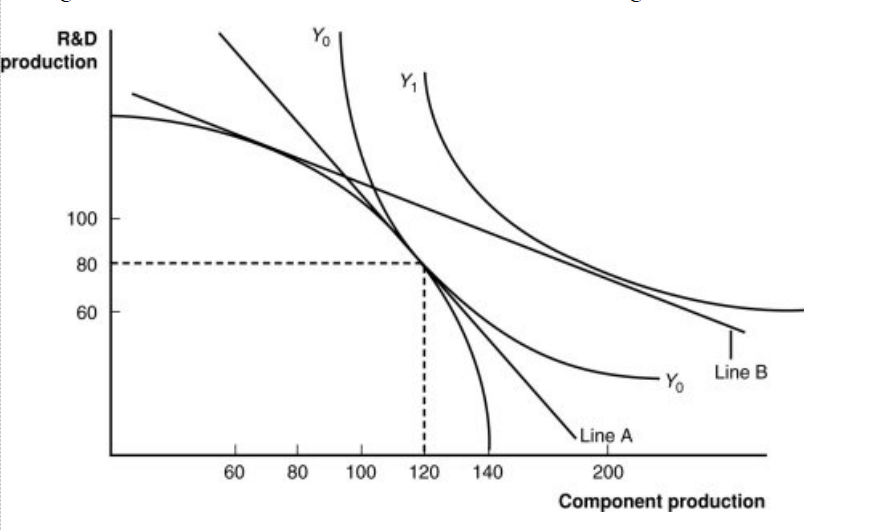
If this firm offshores its component production and exports R&D, how many units of each will it have available in equilibrium?
a. 60 R&D; 120 components
b. 80 R&D; 80 components
c. 100 R&D; 100 components
d. 80 R&D; 200 components
18.
Figure: A Firm’s Production with and Without Offshoring 1

How can we measure this firm’s gains from offshoring?
a. It is represented as the move from Line A to Line B.
b. It is represented as the move from Line A to Y1.
c. It is represented as the move from Y0 to Y1.
d. It is represented as the point where the firm produces 80 units of R&D and 120 components.
19. 国际贸易测试代写
Figure: A Firm’s Production with and Without Offshoring 2
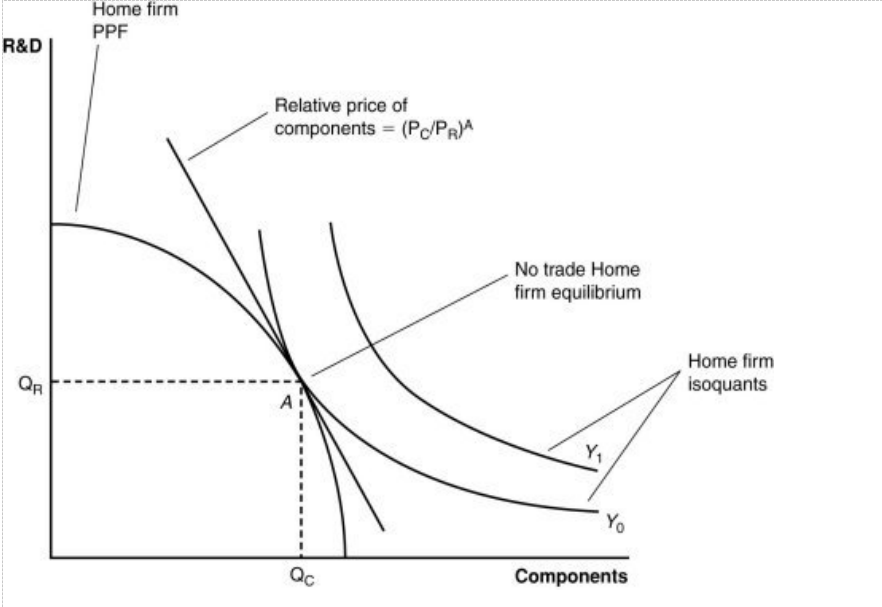
The combination of outputs shown by the isoquant Y1:
a. can be achieved using the present components and R&D in the country.
b. is beyond the nation’s capabilities to produce.
c. could be achieved by trading with another country.
d. is beyond the firm’s capabilities to produce domestically but could be achieved by trading with another country.
20.
Figure: A Firm’s Production with and Without Offshoring 2
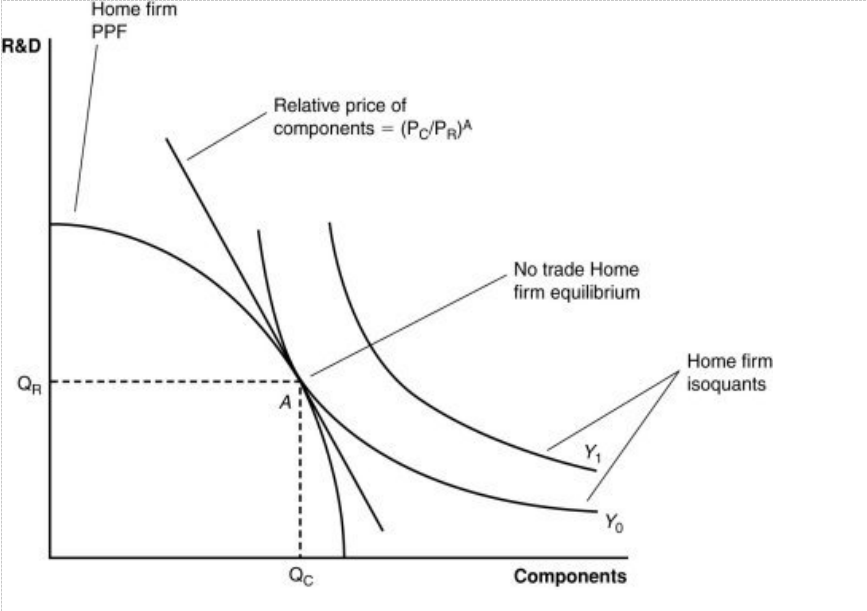
If the relative price of components is cheaper in a foreign country than the home country, then:
a. it is likely that the home country will offshore the R&D to the foreign country.
b. it is likely that the foreign country will offshore the components to the home country.
c. it is likely that the home country will offshore components to the foreign country.
d. no meaningful exchange is possible between the home and foreign countries.
21. 国际贸易测试代写
Figure: A Firm’s Production with and Without Offshoring 2
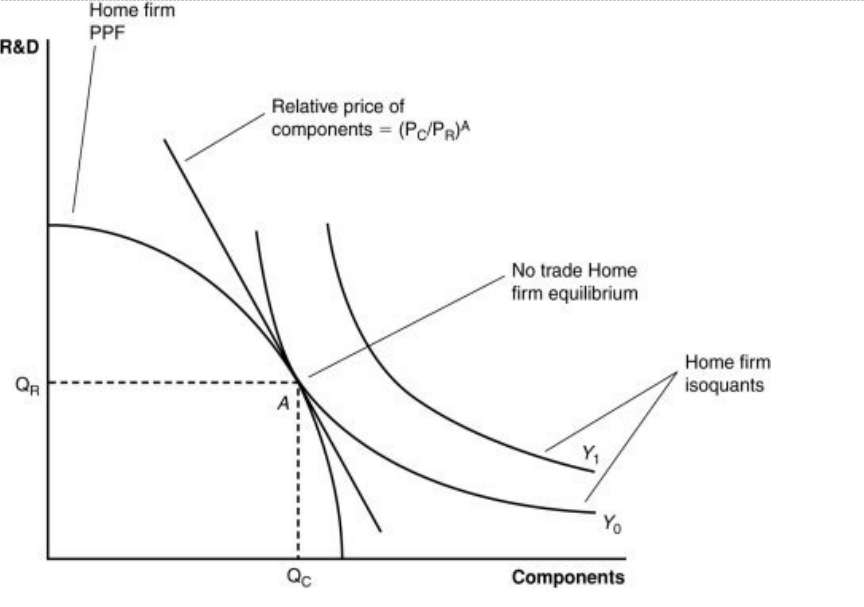
If the home country offshores component production to a foreign country, then exports R&D services to the foreign country and imports components from the foreign country, then:
a. the exchange is not a beneficial one for the home country.
b. the exchange results in an increase in output at lower prices.
c. consumers benefit due to this offshoring.
d. the exchange results in an increase in output at lower prices and consumers benefit due to this offshoring.
22.
Figure: A Firm’s Production with and Without Offshoring 2
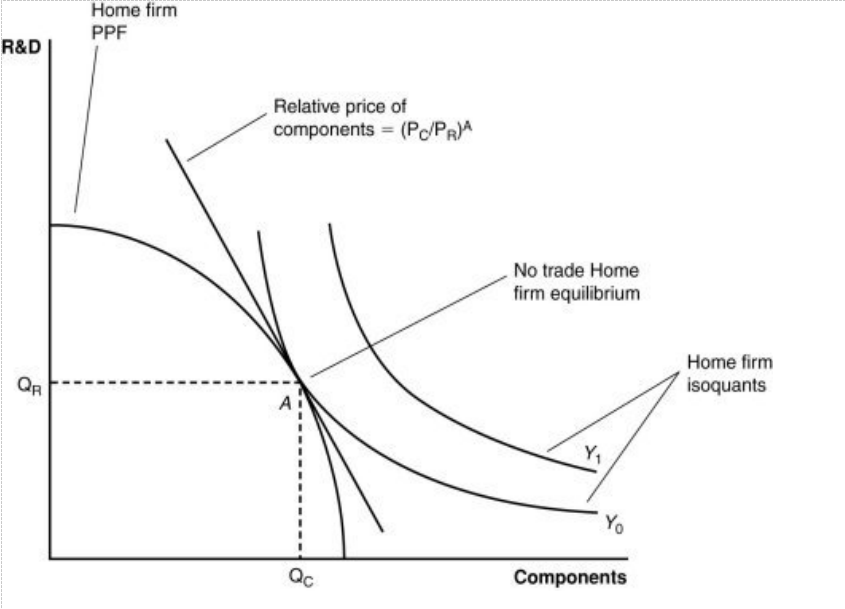
If the world price of components falls, it is likely that:
a. the home country will import more R&D services from the foreign country.
b. the foreign country will produce more R&D services and components for its own domestic use only.
c. the home country will produce more R&D services and trade it for components.
d. there will be no impact on the home country.
23. 国际贸易测试代写
Figure: A Firm’s Production with and Without Offshoring 2
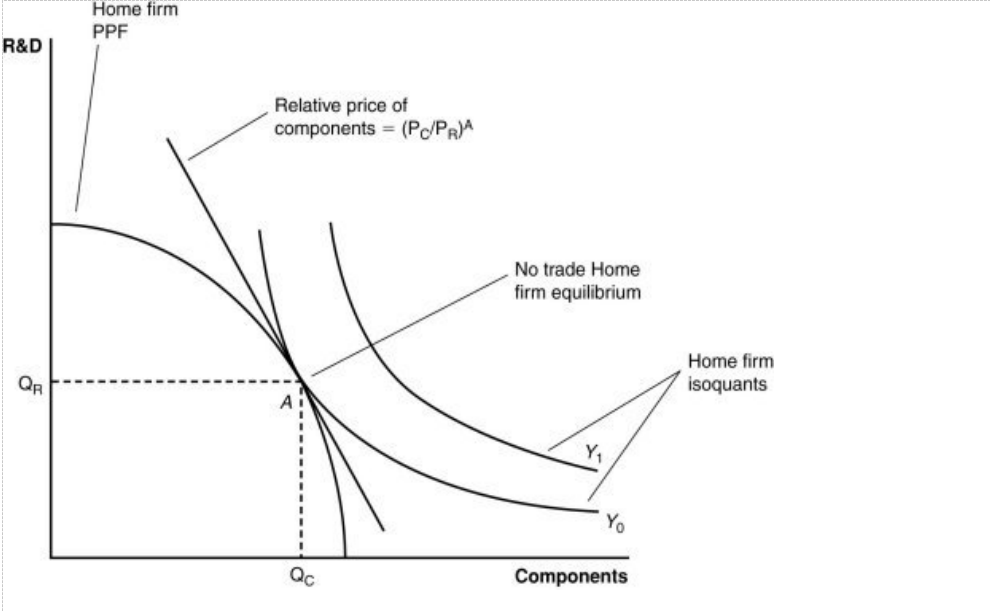
If the price of R&D decreases, then it is likely that the home country:
a. could see a decline in the amount of output produced.
b. will see a loss in comparative advantage in R&D.
c. could see a decline in the amount of output produced and a loss in comparative advantage in R&D.
d. could see an increase in the amount of output produced.
24.
A country will find offshoring attractive when:
a. the international relative price of components is greater than the home price of components.
b. the international relative price of components is less than the home price of components.
c. the home relative price of components falls.
d. the international relative price of research and development falls.
25. 国际贸易测试代写
The economist Paul Samuelson analyzed a scenario in which R&D production suffers from foreign competition, which lowers its price. Samuelson notes that foreign competition in R&D will generally _____ the terms of trade and national welfare if the nation exports R&D.
a. raise
b. lower
c. help
d. not affect
26.
Samuelson says that a fall in the relative price of R&D exports leads to a(n) _____ in the terms of trade and a _____ in export volume. Samuelson’s point is that a country will be _____ than in the absence of trade.
a. improvement; reduction; better off
b. worsening; reduction; better off
c. worsening; reduction; worse off
d. improvement; reduction; worse off
27. 国际贸易测试代写
Offshoring of very-high-skill medical and technology services to other nations seems to contradict the value chain model of offshoring. Which of the following could be a reason?
a. The ratio of wages of lower-skilled workers to higher-skilled workers in these other nations is relatively lower than the same ratio for the United States.
b. The wages of higher-skilled workers (such as accountants) in these other nations are relatively higher than in the United States.
c. Higher-skilled workers in India earn top money for what they do.
d. The wages of higher-skilled workers (such as accountants) in these other nations are relatively lower than in the United States.
28.
Why is the United States more likely to offshore skilled service activities rather than unskilled manufacturing activities to India?
a. Indian trade costs for manufacturing and service activities are uniformly high.
b. Relative wages of less skilled workers are lower in India than in the United States.
c. Indian trade costs associated with service activities are higher than those associated with manufacturing activities.
d. Indian trade costs associated with service activities are lower than those associated with manufacturing activities.
29. 国际贸易测试代写
India has a comparative advantage in service exports for all the following reasons except that:
a. India has a large number of people who are educated and conversant in English.
b. India is 12 hours ahead of Eastern Standard Time, which makes it easier to offshore some jobs.
c. service sector jobs do not require massive infrastructure investment.
d. Indians are closer to Americans for historical reasons, and therefore the two countries like to trade with each other.
30.
Table: Labor Requirements
| Assembly Operations | Component Production | Office Services | R&D | |
| Unskilled labor | U.S.: 4 | U.S.: 3 | U.S.: 2 | U.S.: 1 |
| India: 10 | India: 8 | India: 6 | India: 4 | |
| Skilled labor | U.S.: 2 | U.S.: 2 | U.S.: 2 | U.S.: 2 |
| India: 10 | India: 10 | India: 10 | India: 10 |
The table gives U.S. and Indian labor requirements (hours per unit of output) needed in each of four activities to produce the final product. Suppose that wages of unskilled and skilled workers are $10 and $20 in the United States and $1 and $5 in India, respectively. What is the cost of conducting assembly operations in the United States and India?
a. $6 in the United States and $20 in India
b. $60 in the United States and $20 in India
c. $80 in the United States and $100 in India
d. $80 in the United States and $60 in India
31. 国际贸易测试代写
Table: Labor Requirements
| Assembly Operations | Component Production | Office Services | R&D | |
| Unskilled labor | U.S.: 4 | U.S.: 3 | U.S.: 2 | U.S.: 1 |
| India: 10 | India: 8 | India: 6 | India: 4 | |
| Skilled labor | U.S.: 2 | U.S.: 2 | U.S.: 2 | U.S.: 2 |
| India: 10 | India: 10 | India: 10 | India: 10 |
The table gives U.S. and Indian labor requirements (hours per unit of output) needed in each of four activities to produce the final product. Suppose that wages of unskilled and skilled workers are $10 and $20 in the United States and $1 and $5 in India, respectively. If trade costs are zero, where is the value chain sliced? Which operations will the United States offshore to India?
a. assembly operations
b. assembly operations and component production
c. assembly operations, component production, and office services
d. assembly operations, component production, office services, and R&D
32. 国际贸易测试代写
Table: Labor Requirements
| Assembly Operations | Component Production | Office Services | R&D | |
| Unskilled labor | U.S.: 4 | U.S.: 3 | U.S.: 2 | U.S.: 1 |
| India: 10 | India: 8 | India: 6 | India: 4 | |
| Skilled labor | U.S.: 2 | U.S.: 2 | U.S.: 2 | U.S.: 2 |
| India: 10 | India: 10 | India: 10 | India: 10 |
The table gives U.S. and Indian labor requirements (hours per unit of output) needed in each of four activities to produce the final product. Suppose that wages of unskilled and skilled workers are $10 and $20 in the United States and $1 and $5 in India, respectively. What is the relative wage of skilled labor in the United States?
a. $2/$1
b. $1/$2
c. $4/$1
d. $5/$1
33. 国际贸易测试代写
Reductions in trade costs will tend to:
a. discourage offshoring.
b. discourage foreign production.
c. encourage offshoring.
d. have no immediate effect on offshoring decisions.
34.
As offshoring activities increase, the relative demand for skilled workers in the home nation:
a. will increase.
b. will decrease.
c. will neither increase nor decrease.
d. will raise wages to the point that offshoring no longer becomes a possibility.
35.
When countries open up for offshoring, which country will tend to specialize in research and development?
a. the country abundant in skilled labor
b. the country abundant in unskilled labor
c. neither country
d. both countries


